Lagos (Yoruba: Èkó) is a city in the Nigerian state of Lagos. The city, with its adjoining conurbation, is the largest in Nigeria, as well as on the African continent. It is one of the fastest growing cities in the world and also one of the most populous urban agglomerations in the world. Lagos is a major financial centre in Africa; the mega city has the highest GDP, and also houses one of the largest and busiest ports on the continent.
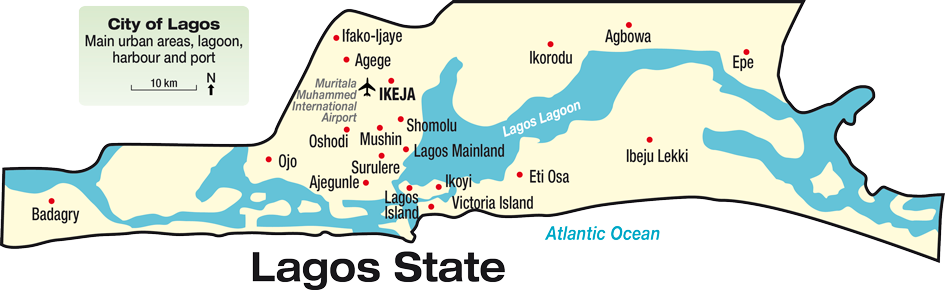
Lagos initially emerged as a port city which originated on a collection of islands, which are contained in the present day Local Government Areas (LGAs) of Lagos Island, Eti-Osa, Amuwo-Odofin and Apapa; the islands are separated by creeks, fringing the southwest mouth of Lagos Lagoon, while protected from the Atlantic Ocean by barrier islands and long sand spits such as Bar Beach, which stretch up to 100 km (60 mi) east and west of the mouth. Due to rapid urbanization, the city expanded to the west of the lagoon to include areas in the present day Lagos Mainland, Ajeromi-Ifelodun and Surulere. This led to the classification of Lagos into two main areas – the Island, which was the initial city of Lagos, before it expanded into the area known as the Mainland. This city area was governed directly by the Federal Government through the Lagos City Council, until the creation of Lagos State in 1967, which led to the splitting of Lagos city into the present day seven Local Government Areas (LGAs), and an addition of other towns (which now make up 13 LGAs) from the then Western Region, to form the state.
Lagos which was the capital of Nigeria since its amalgamation in 1914, went on to become the capital of Lagos State, after its creation. However, the state capital was later moved to Ikeja in 1976, while the federal capital also moved to Abuja in 1991. Even though Lagos is still widely referred to as a city, the present day Lagos, also known as “Metropolitan Lagos”, and officially as “Lagos Metropolitan Area” is an urban agglomeration or conurbation, consisting of 16 LGAs, including Ikeja, the state capital of Lagos State. This conurbation makes up 37% of Lagos State’s total land area, but houses about 85% of the state’s total population. The population of Metropolitan Lagos is approximately 20 million as at 2015.
Lagos was originally inhabited by the Awori subgroup of the Yoruba people in the 15th century, who called it “Oko”. Under the leadership of the Oloye Olofin, the Awori moved to an island now called Iddo and then to the larger Lagos Island. In the 16th century, the Awori settlement was conquered by the Benin Empire and the island became a Benin war-camp called “Eko” under Oba Orhogba, the Oba of Benin at the time. Eko is still the native name for Lagos.
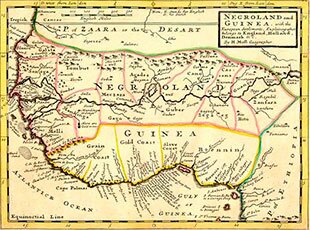
Lagos, which means “lakes”, was a name given to the settlement by the Portuguese. The present-day Lagos state has a high percentage of Awori, who migrated to the area from Isheri along the Ogun river. Throughout history, it was home to a number of warring ethnic groups who had settled in the area. Following its early settlement by the Awori nobility, and its conquest by the Bini warlords of Benin, the state first came to the attention of the Portuguese in the 15th century.
Portuguese explorer Rui de Sequeira visited the area in 1472, naming the area around the city Lago de Curamo. Another explanation is that Lagos was named for Lagos, Portugal – a maritime town which, at the time, was the main centre of Portuguese expeditions down the African coast.
In Britain’s early 19th century fight against the transatlantic slave trade, its West Africa Squadron or Preventative Squadron as it was also known, continued to pursue Portuguese, American, French, and Cuban slave ships and to impose anti-slavery treaties with West African coastal chiefs with so much doggedness that they created a strong presence along the West African coast from Sierra Leone all the way to the Niger Delta (today’s Nigeria) and as far south as Congo. In 1849, Britain appointed John Beecroft Consul of the Bights of Benin and Biafra, a position he held (along with his governorship of Fernando Po) until his death in 1854. John Duncan was appointed Vice Consul and was located at Wydah. At the time of Beecroft’s appointment, the Kingdom of Lagos (under Oba Kosoko) was in the western part of the Consulate of the Bights of Benin and Biafra and was a key slave trading port. In 1851 and with pressure from liberated slaves who now wielded political and business influence, Britain intervened in Lagos in what is now known as the Bombardment of Lagos or Capture of Lagos resulting in the installation of Oba Akitoye (and the ouster of Oba Kosoko) who signed Treaty Between Great Britain and Lagos, 1 January 1852. The signing of the 1852 treaty ushered in the Consular Period in Lagos’ history wherein Britain provided military protection to Lagos.
Following threats from Kosoko and the French who were positioned at Wydah, a decision was made by Lord Palmerston (British Prime Minister) who noted in 1861, “the expediency of losing no time in assuming the formal Protectorate of Lagos”. William McCoskry, the Acting Consul in Lagos with Commander Bedingfield convened a meeting with Oba Dosunmu on July 30, 1861 aboard HMS Prometheus where Britain’s intent was explained and a response to the terms were required by August 1861. Dosunmu resisted the terms of the treaty but under the threat to unleash violence on Lagos by Commander Bedingfield, Dosunmu relented and signed the Lagos Treaty of Cession on August 6, 1861.
The remainder of modern-day Nigeria was seized in 1887, and when the Colony and Protectorate of Nigeria was established in 1914, Lagos was declared its capital, continuing as such after the country’s independence from Britain in 1960. Along with migrants from all over Nigeria and other West African nations were the returnee ex-slaves known as Creoles, who came from Freetown, Sierra Leone, Brazil and the West Indies to Lagos. The Creoles contributed to Lagos’ modernisation and their knowledge of Portuguese architecture can still be seen from the architecture on Lagos Island. Electric street lighting was introduced in the city in 1898. Lagos experienced rapid growth throughout the 1960s and 1970s as a result of Nigeria’s economic boom.
Before the creation of Lagos State on 27 May 1967, Lagos, which was the country’s capital had been administered directly by the Federal Government as a Federal Territory through the Federal Ministry of Lagos Affairs, while the Lagos City Council (LCC) governed the city. Lagos, along with the towns from the then Western region (Ikeja, Agege, Mushin, Ikorodu, Epe and Badagry), were eventually captured to create Lagos State. Lagos city was split into the present day seven Local Government Areas(LGAs), while the other towns now make up 13 LGAs in the state. Lagos played the dual role of being the State and Federal Capital until 1976, when the state capital was moved to Ikeja. Lagos was adversely affected during Nigeria’s military rule. Also, on 12 December 1991, the seat of the Federal Government was also formally relocated to Abuja. However, Lagos still remains the financial centre of the country, and also grew to become the most populous conurbation in the country.